Math & Geometry
Apply mathematical concepts to algorithmic problems.
8
Problems
2
Easy
6
Medium
0
Hard
How Math & Geometry Works
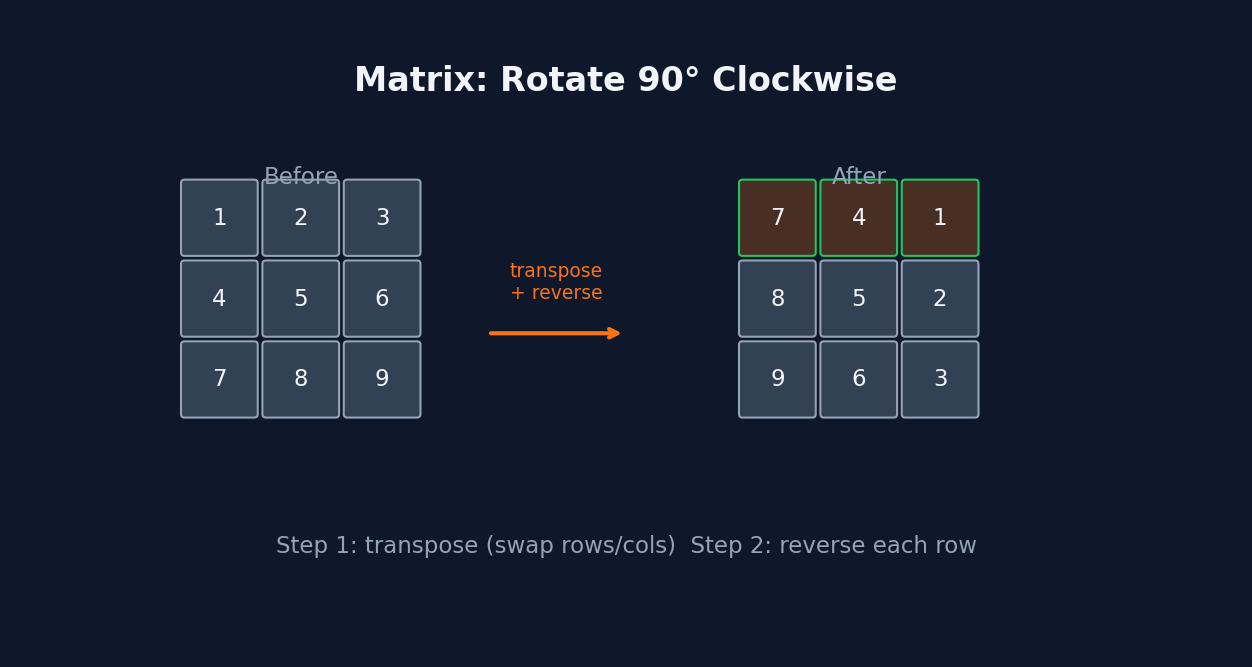
Math and Geometry problems use mathematical properties and formulas to find efficient solutions. Common techniques include modular arithmetic (for large numbers), the GCD/LCM for divisibility problems, matrix operations for grid rotations, and mathematical formulas to avoid brute-force counting. For geometry, key concepts are coordinate math, distance formulas, and understanding how rotations and reflections map coordinates. Often the trick is recognizing a mathematical pattern that eliminates the need for simulation.
When to Use Math & Geometry
Pattern Recognition
Look for these trigger words in problem statements:
rotate image
math-and-geometry
spiral matrix
set matrix zeroes
happy number
plus one
pow(x, n)
multiply strings
detect squares
Common Mistakes
- Integer overflow when multiplying large numbers (use modular arithmetic or long/BigInt)
- Floating-point precision errors in geometry (use integer math where possible)
- Not handling negative numbers or zero as edge cases
- Overcomplicating with code when a formula or mathematical property gives a direct answer
When NOT to Use Math & Geometry
- When there's no mathematical shortcut and simulation is the only approach
- When the problem is fundamentally about data structures, not math
- When the mathematical solution is too complex and a simpler algorithmic approach works
Practice Problems
Master Math & Geometry
Build pattern recognition with interactive MCQs. Understand why to use Math & Geometry, not just how.
Download LeetEye Free