Heap / Priority Queue
Maintain priority with heap-based data structures.
7
Problems
0
Easy
0
Medium
7
Hard
How Heap / Priority Queue Works
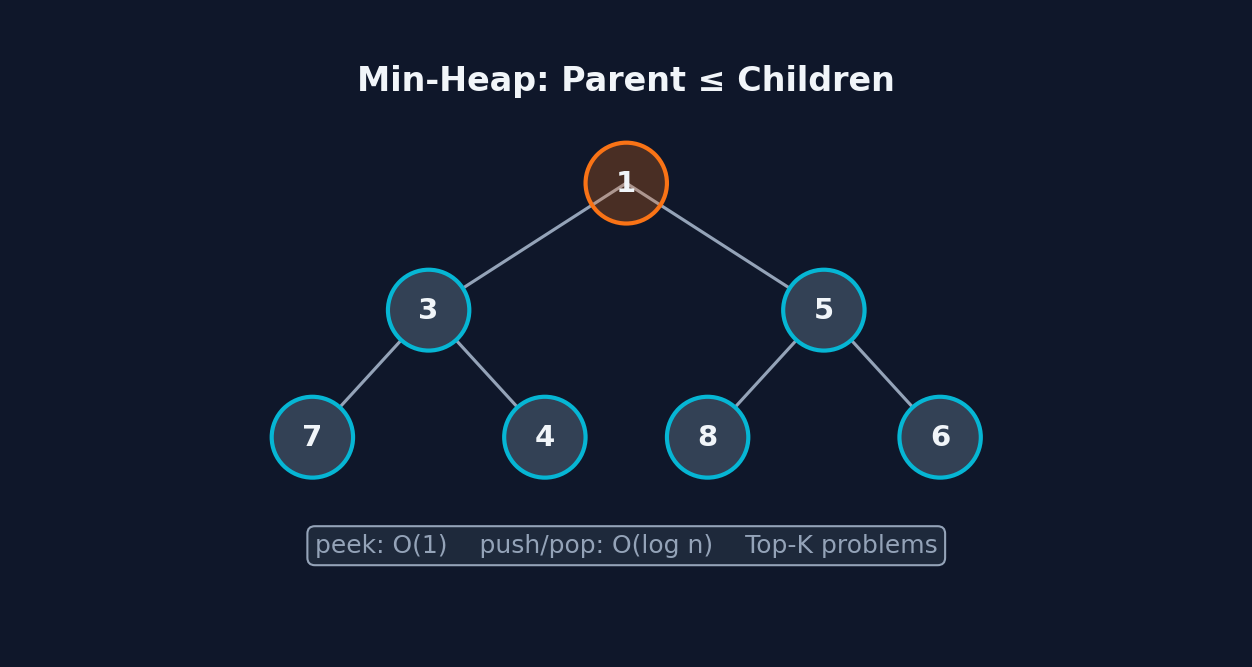
A Heap (Priority Queue) maintains elements in a partially ordered structure where the min (or max) element can be accessed in O(1) and extracted in O(log n). This is essential for "top K" problems, stream processing, and merge operations. For "K smallest/largest" problems, use a max-heap of size K — when it exceeds K elements, pop the max, guaranteeing the K smallest remain. Two heaps (max-heap + min-heap) can maintain a running median by balancing elements between them.
When to Use Heap / Priority Queue
Pattern Recognition
Look for these trigger words in problem statements:
kth largest element in a stream
heap
last stone weight
k closest points to origin
kth largest element in an array
task scheduler
design twitter
find median from data stream
Common Mistakes
- Using the wrong heap type — Python's heapq is a min-heap; negate values for max-heap
- Forgetting that heap operations are O(log n), not O(1) for insertion
- Not maintaining the correct heap size for K-element problems
- Trying to remove arbitrary elements from a heap (use lazy deletion or a different data structure)
When NOT to Use Heap / Priority Queue
- When you need the full sorted order (just sort the array)
- When K is close to N (sorting is simpler and equally efficient)
- When you need to access elements by index (use a sorted array or balanced BST)
Practice Problems
Compare With Other Patterns
Master Heap / Priority Queue
Build pattern recognition with interactive MCQs. Understand why to use Heap / Priority Queue, not just how.
Download LeetEye Free