Bit Manipulation
Leverage binary operations for space and time efficiency.
7
Problems
5
Easy
2
Medium
0
Hard
How Bit Manipulation Works
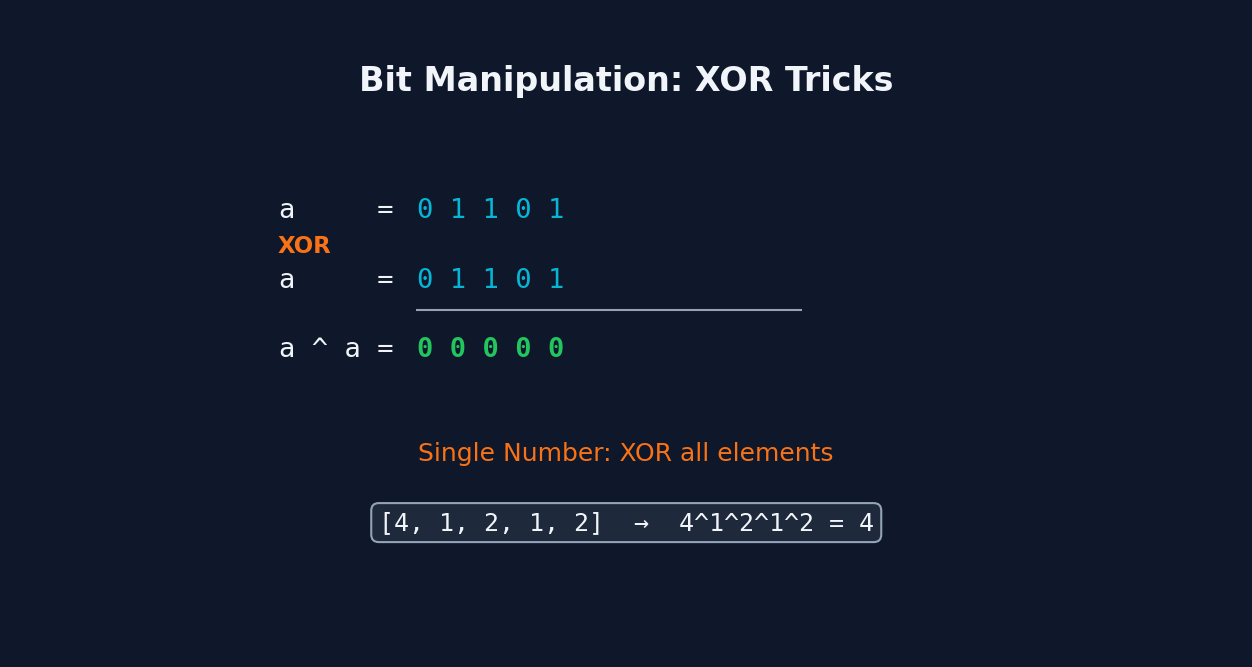
Bit manipulation operates directly on the binary representation of numbers using bitwise operators: AND (&), OR (|), XOR (^), NOT (~), and shifts (<<, >>). XOR is especially powerful: a ^ a = 0 and a ^ 0 = a, so XORing all elements cancels out pairs, leaving the unique element. Common tricks include n & (n-1) to clear the lowest set bit, n & (-n) to isolate the lowest set bit, and bit masks to track state in O(1) space. This enables solving certain problems without extra data structures.
When to Use Bit Manipulation
Pattern Recognition
Look for these trigger words in problem statements:
single number
bit-manipulation
number of 1 bits
counting bits
reverse bits
missing number
sum of two integers
reverse integer
Common Mistakes
- Operator precedence errors — bitwise operators have lower precedence than comparison operators in most languages
- Not considering signed vs unsigned integers (negative numbers have different bit patterns)
- Assuming 32-bit integers when the problem uses different sizes
- Overcomplicating solutions — bit manipulation should simplify, not obscure the logic
When NOT to Use Bit Manipulation
- When a hash set or hash map solution is clearer and equally efficient
- When the numbers are too large for fixed-width bit operations
- When the bit manipulation trick is obscure and makes the code unreadable
Practice Problems
Master Bit Manipulation
Build pattern recognition with interactive MCQs. Understand why to use Bit Manipulation, not just how.
Download LeetEye Free