Arrays & Hashing
Master the fundamentals of arrays and hash-based data structures for O(1) lookups.
8
Problems
8
Easy
0
Medium
0
Hard
How Arrays & Hashing Works
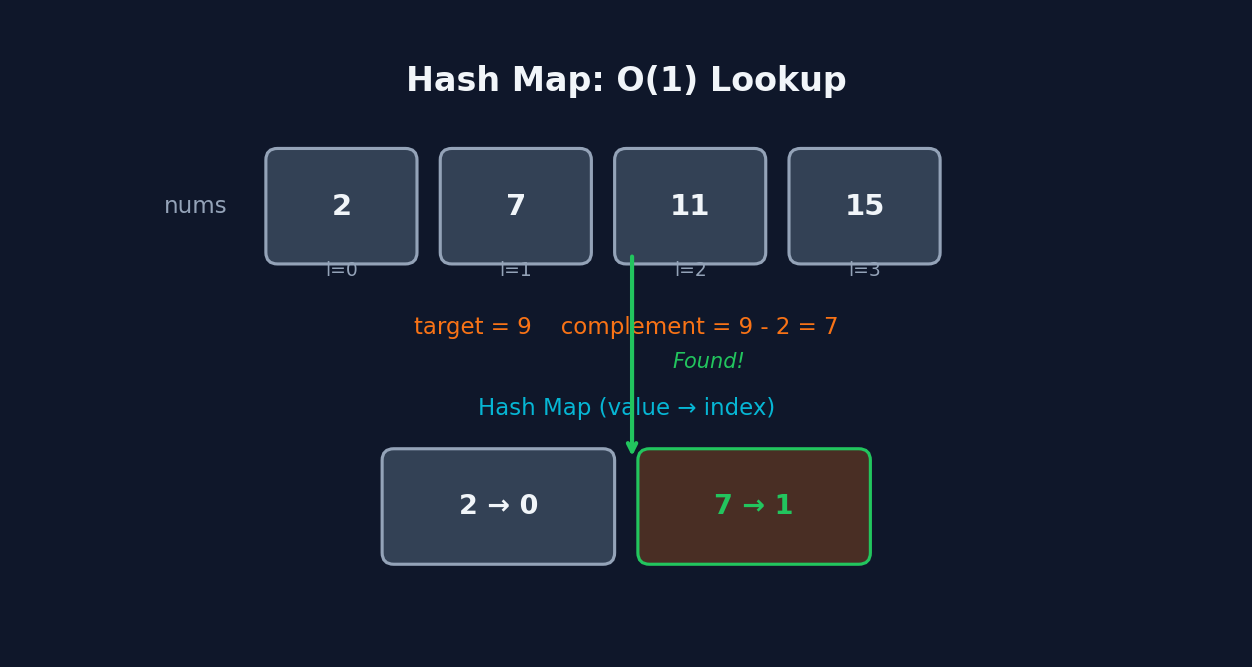
Arrays and Hashing combines two fundamental concepts: sequential data storage and constant-time lookups. The core idea is to use a hash map (dictionary) to store seen values while iterating through an array, enabling O(1) lookups instead of O(n) nested searches. This transforms brute-force O(n²) solutions into O(n) single-pass algorithms. The hash map acts as a memory of what you've encountered, letting you answer questions like "have I seen this before?" or "what pairs with this value?" instantly.
When to Use Arrays & Hashing
Pattern Recognition
Look for these trigger words in problem statements:
contains duplicate
arrays-and-hashing
valid anagram
two sum
group anagrams
top k frequent elements
product of array except self
valid sudoku
longest consecutive sequence
Common Mistakes
- Forgetting to handle duplicate elements in the hash map
- Using a hash set when you need to track indices (use a hash map instead)
- Not considering that hash maps use O(n) extra space
- Modifying the array in-place when the problem expects the original order preserved
When NOT to Use Arrays & Hashing
- When the array is already sorted (two pointers is more space-efficient)
- When you need to find elements in a specific range (binary search is better)
- When memory is extremely constrained and O(1) space is required
Practice Problems
Master Arrays & Hashing
Build pattern recognition with interactive MCQs. Understand why to use Arrays & Hashing, not just how.
Download LeetEye Free