Advanced Graphs
Master complex graph algorithms like shortest paths and minimum spanning trees.
6
Problems
0
Easy
0
Medium
6
Hard
How Advanced Graphs Works
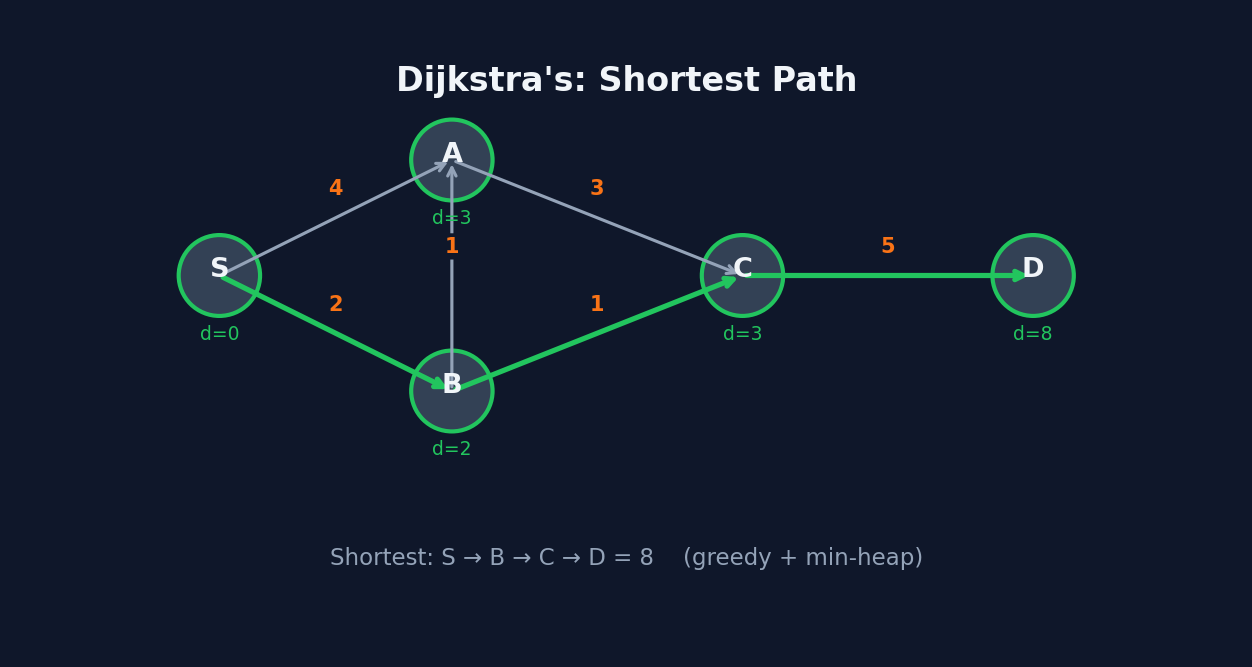
Advanced graph algorithms handle weighted edges, shortest paths, and minimum spanning trees. Dijkstra's algorithm finds shortest paths from a source using a priority queue, always expanding the closest unvisited node. Bellman-Ford handles negative weights by relaxing all edges V-1 times. Kruskal's and Prim's algorithms find minimum spanning trees. Topological sort orders nodes in a DAG so every edge goes from earlier to later, essential for dependency resolution.
When to Use Advanced Graphs
Pattern Recognition
Look for these trigger words in problem statements:
min cost to connect all points
advanced-graphs
network delay time
swim in rising water
alien dictionary
cheapest flights within k stops
reconstruct itinerary
Common Mistakes
- Using Dijkstra with negative edge weights (it won't work — use Bellman-Ford)
- Not using a priority queue for Dijkstra, resulting in O(V²) instead of O((V+E)log V)
- Forgetting to detect negative cycles with Bellman-Ford
- Applying topological sort to a graph with cycles (it only works on DAGs)
When NOT to Use Advanced Graphs
- When all edges have equal weight (use simple BFS for shortest path)
- When the graph is small enough for brute-force approaches
- When the problem doesn't actually need shortest paths or spanning trees
Practice Problems
Master Advanced Graphs
Build pattern recognition with interactive MCQs. Understand why to use Advanced Graphs, not just how.
Download LeetEye Free